Blockchain business models: a comprehensive guide
Blockchain businesses still remain highly sought after by investors and actively explored by end-customers.
Blockchain is a universal technology, which can be easily adopted in any field and introduced to various types of audiences. This is why there is constant development of new business models and applications for the technology. We’ll take a look at the most common blockchain business models and analyze their practical applications.
What is a blockchain-based business model?
Blockchain business models are peer-to-peer networks based on decentralized transactions that use crypto coins and tokens to make a profit and provide users with exchanging services or goods.
The decentralized structure of blockchain lies at the core of business operations, data storage, profit collection, business growth. Blockchain is used to assure that end users have a secure and transparent environment for data management, transactions, communication with other users, etc. What's more, it provides an insight into any data manipulation, highlighting and exposing potential cybercrime attempts before they have a chance to materialize that makes blockchain a potentially strong cybersecurity business model. Sounds impressive, right? Let’s examine how blockchain business models allow achieving better cybersecurity and can be adopted in different niches.
Traditional business models
A business model is a strategy used by the company to make a profit from a service or product. It’s the plan that the company uses to monetize business activities. Business models can differ depending on the market and type of offered products/services, but generally, there are four main traditional models. Let’s find out more details below:
Manufacturer
This business model implies that the company creates a product - either from scratch or with existing details (like vehicles). Manufacturing businesses can target the end customer - the B2C business model, but they also can rely on other businesses - in this case, the primary goal is to increase the number of partnerships and distributors (a B2B model).
Distributor
Distributors don’t create products, but instead, partner with companies who do - manufacturers. They can sell the products to retailers or end-users. Services also can be distributed by independent companies - online marketplaces, for instance, act like distributors because they don’t provide services or goods, but connect those who do with end buyers.
Retailer
Retailers are companies whose main goal is to connect the end-user with the product. They don’t take care of technical production aspects - retailers mostly work with distributors or manufacturers. Retailers can also be distributors if they make direct partnerships with manufacturers. The main goal of such a company is to make sure they are easily available to the end customer and attract consumers to the product via sales and marketing.
Franchise
The franchise model can be any of the described above. The only reason is, this company allows purchasing its business model, technology, and style to open the points-of-sale for the franchise. Business relies on independent parties to expand its reach, receiving the commission in return.
Secure blockchain-based business models
Digital services use mentioned above traditional models and adapt them depending on technology. Blockchain doesn’t entirely refuse the ideas of the traditional economy, benefiting from their principles, but it also builds a new, safe way of approaching business, based on its algorithms.
Blockchain as a Service (BaaS)
Blockchain as a Service is the creation of cloud-based software for companies that build blockchain apps. Such software is available to users on a subscription basis - customers pay a monthly fee and receive access to all updates, tech support, and additional resources. The subscriptions can differ in their functionality - premium plans can include improved features, team access, or direct tech support.
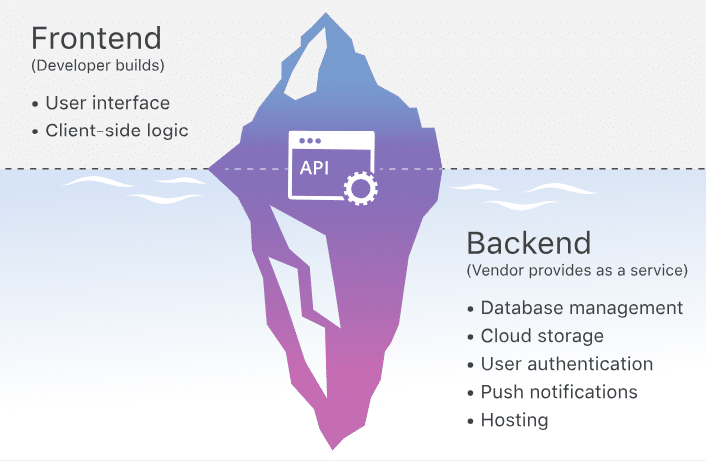
BaaS was inspired by Software as a Service model - a model where software is provided not like a product, bought once and for all, but a continuous service, for a monthly subscription. The business model is focused on providing highly advanced cybersecurity - users should be able to work with their networks in a safe environment - this is achieved with advanced encryption and decentralization - the data from BaaS is stored on all nodes.
Security benefits
Such a model makes use of cloud services to let users build, manage, and host their blockchain apps, using ready blockchain networks. Customers can rely on third-party’s computing power, and they don’t have to create own nodes. They don’t have to create own encryption mechanisms or worry protecting a centralized data storage - the service provider stores all data in the safe blockchain metric.
Moreover, the blockchain as a service providers have to manage the back-end services, specifically the complicated services for clients and businesses. It is their responsibility to look after the crucial blockchain technology artifacts and keep them running without any downtimes.
Blockchain services also include hosting requirements and security protocols like distribution of resources, anti-hack layering, bandwidth management and much more.
Examples of BaaS
- Microsoft’s partnership with ConsenSys - together the companies created a service on Microsoft Azure that supports Ethereum’s tokens and smart contracts. Users can create custom tokens and write smart contracts, using a ready network.
- Amazon Managed Blockchain - a service for the creation and management of blockchain networks, powered by open-source tools.
- R3 - a project, backed up by major financial institution that gives business access to Corda, a decentralized financial ledger.
- PayStand - a blockchain platform that allows a business to use their tools for integrating blockchain payments to their websites. Businesses can accept crypto coins and pay with them.
Implementing blockchain independently is a challenge for business owners because it’s a complex technology that requires a lot of computing power. BaaS makes blockchain more accessible by providing all infrastructure and established network. The provider takes responsibility for all backend processes. BaaS platforms implement cybersecurity, bandwidth management, resource allocations, etc.
Token Economy - Utility Token Business Model
Tokenization is the process of using tokens to represent currencies, services, products, and any kind of assets. Blockchain uses cryptographic tokens - a digital form of an asset that is connected to a blockchain network - to allow users to receive goods and services on a decentralized platform, as well as invest in the platform.
Security benefits
By purchasing tokens, users are connected either directly to the company (becoming an investor) or become an active part of the blockchain-based marketplace (acquiring rights to purchase goods and services, available on the platform.) It’s a safe way to perform a transaction that doesn’t depend on a particular location. Unlike in typical bank transfers, there is no single bank entity that needs to approve the payment - it’s easier to hack into a single system rather than each of thousands of network devices.
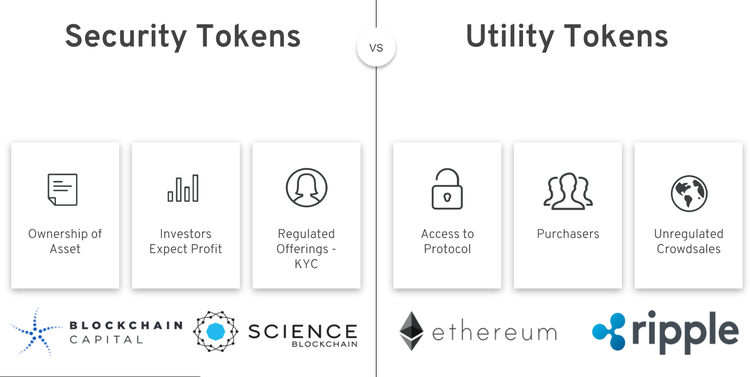
Possible uses of blockchain tokens
- Investing - blockchain businesses make tokens available for purchase at the initial stages of company development. Users who buy tokens, can receive a percentage from business profits - as regular investors - or use these tokens later to purchase services on the platform. This form of cooperation is known as crowdfunding and is usually done via Initial Coin Offerings.
- Blockchain-based marketplace. Some blockchain platforms allow users to sell and buy goods on the platform, becoming a peer-to-peer marketplace. For instance, on OpenBazaar, a blockchain-based online store, the customer can purchase goods all over the world with tokens with no commission, and put own items for sale - there is a constant flow of tokens from one user to another.
- Currency exchange After a token becomes popular enough, businesses partner with other currencies and crypto wallets, enabling the safe token exchange. Less popular custom coins can be exchanged for more common cryptocurrencies - Bitcoin, Ether, LiteCoin. This gives a holder of the token a possibility to purchase almost anything, not just a service, available on the platform.
Tokens that can be used on the blockchain platform is a utility token used to get access to features or receive services from other users. Some tokens allow users to vote on certain issues (for instance, if a user purchased a token of a sports club, they might get the right to vote on management decisions), others reward users for their work for the community and can be exchanged for Bitcoin, but not spent on the service.
Blockchain-based Software Products
Blockchain-based software products are represented by tools that use blockchain for some features - secure data storage, documentation management, or analytics. Let’s see what characteristics of blockchain are most useful for blockchain-based software and how it’s applied in different industries.
Security benefits
Decentralization: in traditional business models, the data is stored on a single centralized server. It’s easy to target a single server and put in jeopardy important data, like financial, medical, or governmental records. For instance, software developers, who work in healthcare, often use blockchain to improve safety - medical data is stored on all devices that are connected to the blockchain network, rather than just on one.
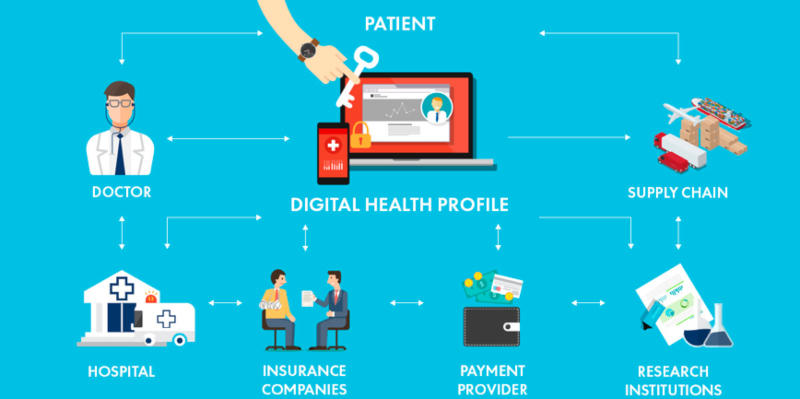
Crypto transactions: blockchain-based transactions allow making safe international payments with low commission or no money. This feature of blockchain is attractive to fintech developers, who want to make secure international transactions available to wide audiences. Many tools are based on providing blockchain-based payments as well as exchanging cryptocurrencies for traditional ones.

Smart contracts: Ethereum-based contracts are the sets of algorithms that determine agreements’ conditions. As soon as the requirements are met, the contract is executed automatically. This application of blockchain is useful in fields like real estate or insurance, where the process of preparing the documentation is slow and disorganized. Smart contracts help to define objective requirements for the deal and deprive parties of the right to suddenly change their minds.
To sum up, blockchain-based software is a tool that targets businesses and end customers by offering blockchain-powered features that solve some of the market’s urgent issues and cybersecurity threats coming from attackers. Usually, such products emphasize on delivering safe and transparent experience, which becomes possible due to blockchain’s decentralization and ability to store a full transaction history.
How can a blockchain business model secure your business?
Blockchain business models solve a lot of problematic issues of traditional business models. Let’s take a look at the main ones.
- Transparency. Blockchain network stores all the information about each transaction. At any given moment, a user can see who performed the transaction and track the entire history of the block. It increases trust between users and the company.
- Global impact. Cryptocurrencies aren’t tied to the local economy, which makes them resistant to political changes. It also means all users are equal, regardless of their location.
- Security. The data is stored not on a single server but a decentralized network. If your business uses a traditional database, you will need to invest a lot of resources in securing it. Blockchain, however, is secure by design - all data is stored on multiple devices, and hackers can’t get access to it - security is achieved by default.
- Investment value. Investors are constantly looking for companies that can find a useful application to blockchain and solve real problems.
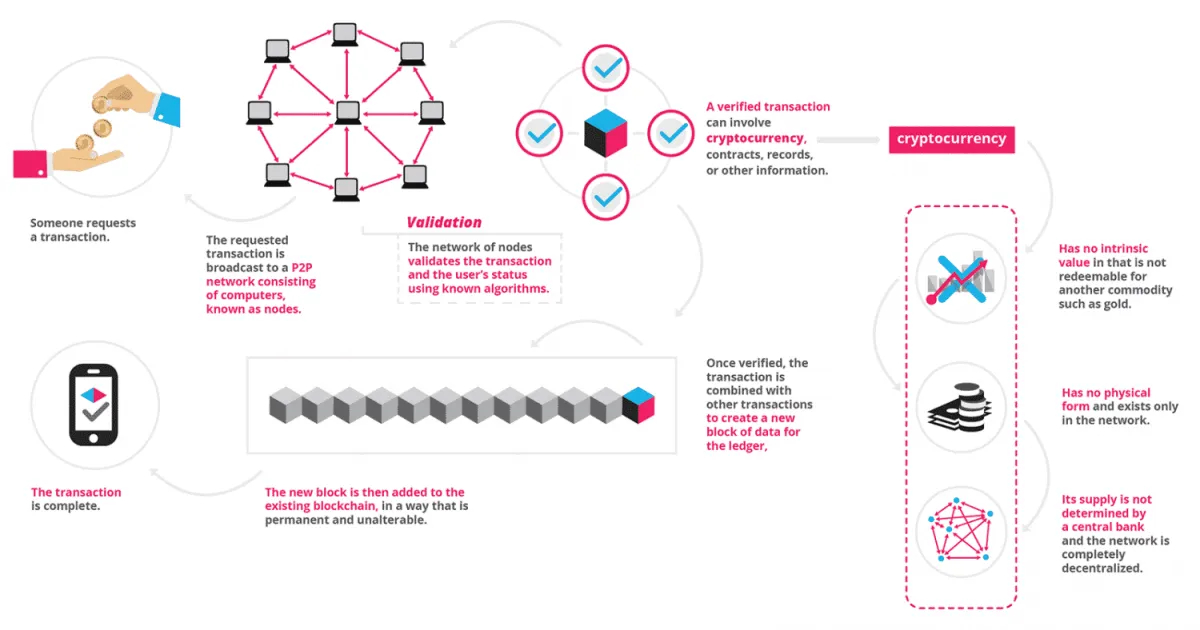
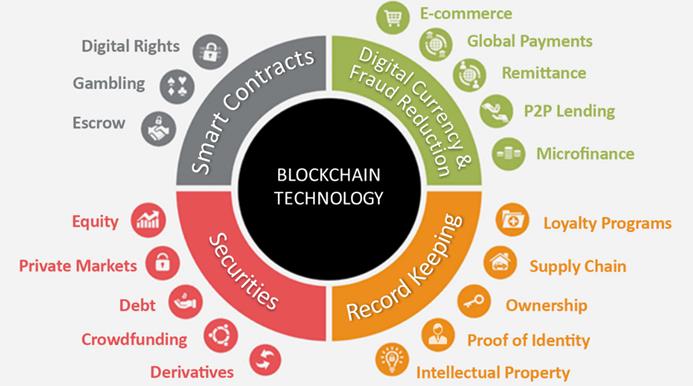
Blockchain’s benefits can be applied to any field - from fintech to real estate. Commission-free transactions, automatically executable smart contracts, and secure data storage - these tangible advantages that any online business can profit from.
Bottom line
Blockchain business models bring value both to the end-users and business owners. Users can know that their data is stored safely, get a full history of their transactions, and create reliable agreements with smart contracts. Business owners can accept payments all over the world, attract investors, and reduce the number of required security investments.
The blockchain market keeps growing every year, and we are only starting to unravel its potential. Already, it’s apparent that blockchain can answer a lot of our current questions about cybersecurity and global cooperation - but it’s just the tip of the iceberg. The niche is still waiting for global disruptive solutions - and business owners are welcome to jump on board.
Related Posts
Blockchain technology has entered a new era of innovation and trust in our digital world today.
The high interest in blockchain and cryptocurrency has impacted financial institutions. Currently, the influence of these new technologies on the banking system is being actively studied.
Some people tend to use cryptocurrencies as a means of payment. Indeed, digital assets are accepted as a payment method in some shops and restaurants.
Cryptocurrencies offer many advantages. They are easy for paying for goods and services, sending funds abroad without fees, and you can even earn money on the cryptocurrency market.
Bitcoin investment is the largest in the crypto sector today.
There’s no doubt cryptocurrency, and its incorporation into everyday life is here to stay.
















Comments
comments powered by Disqus